Rossby modes
The (linearized) momentum equation governing the dynamics of a fluid at a surface of the sphere with radius
where
Looking for oscillatory solutions with time-dependence proportional to
which may be rewritten as:
where
provided that the frequency satisfies the following dispersion relation:
These solutions are called Rossby modes. The first few of these are plotted here below on the Earth’s surface. From top to bottom:
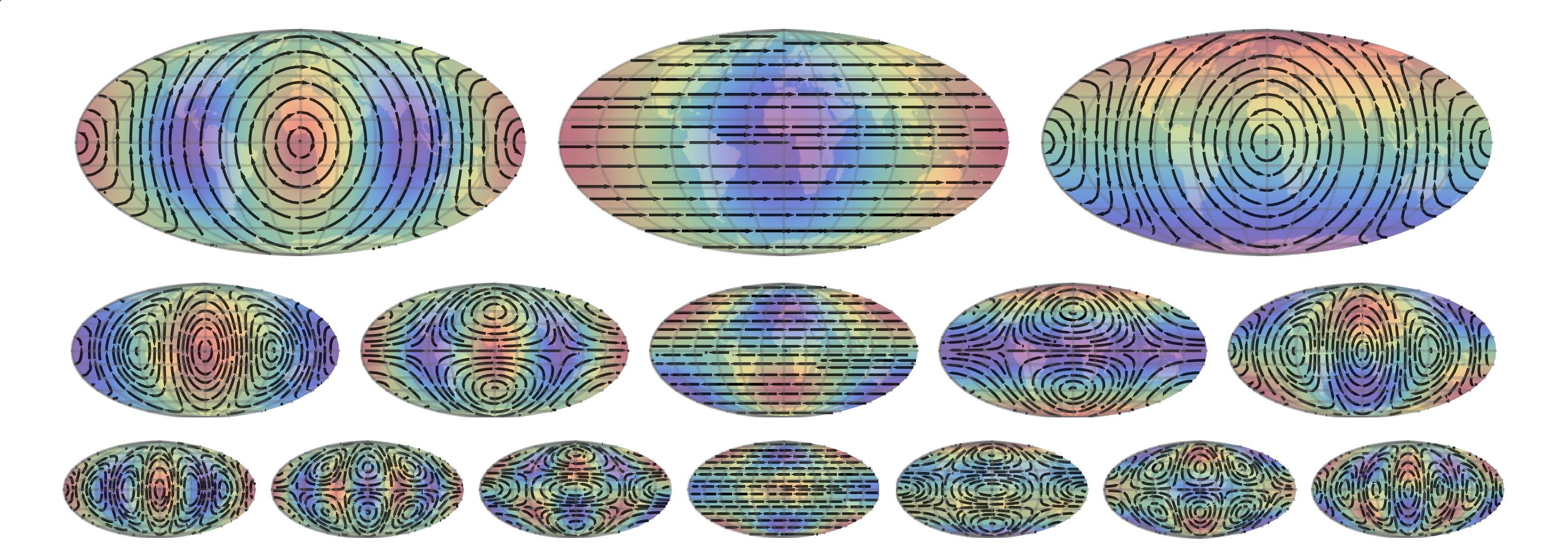
References
- Longuet-Higgins, M. S. Planetary waves on a rotating sphere. II (1965) ,Proc. R. Soc. Ser. A,284, 40
- Zaqarashvili et al. Rossby Waves in Astrophysics (2021)